- Products
- Pressure Reducing Regulators
- Back Pressure Regulators
- Tank Blanketing Valves
- Temperature Regulators
- Industrial Control Valves
- Wafer Style Control Valves
- JCVS Industrial Control Valves
- Globe Style/Cage Guided Control Valves
- Mixing/Diverting Control Valves
- Motor Operated Control Valves
- Valve Positioners & Accessories
- Applications
- Resources
- Find a Sales Rep
- Brands
Top 10 Pressure Reducing Valves: Essential Features and Benefits Explained
In the modern landscape of industrial applications, Pressure Reducing Valves (PRVs) play a critical role in ensuring operational efficiency and safety. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global PRV market is projected to grow significantly, with a CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026, reflecting a growing demand for effective pressure management systems across various sectors, including water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing. The ability of PRVs to stabilize and minimize pressure fluctuations not only protects sensitive equipment but also enhances energy efficiency, making them indispensable in today’s industrial processes.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Chen, a leading authority on fluid dynamics, emphasizes the importance of these devices, stating, “The selection of the right Pressure Reducing Valve is crucial in improving system performance and prolonging equipment life.” As industries face increasing pressure to optimize performance and reduce operational costs, understanding the features and benefits of PRVs becomes essential for engineers and decision-makers alike. Our exploration of the top 10 Pressure Reducing Valves will shed light on key attributes and advantages that can drive effective pressure management in various applications, safeguarding investments and promoting sustainability.

Understanding Pressure Reducing Valves: An Overview
Pressure reducing valves (PRVs) play a vital role in various systems by controlling and regulating the pressure of fluids. These devices are essential in preventing damage to pipelines and equipment caused by high pressure. By maintaining consistent downstream pressure, PRVs ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system. The basic operation of a PRV involves adjusting the flow rate based on preset pressure levels, allowing for the safe use of fluids across different applications, from residential plumbing to industrial processes.
Tips for selecting a pressure reducing valve include assessing the specific needs of your system, including the inlet and outlet pressure requirements. It's crucial to consider the maximum flow capacity and the type of fluid involved to avoid compatibility issues. Additionally, look for features such as temperature tolerance and corrosion resistance which can significantly impact the valve's performance and lifespan.
When installing a PRV, ensure it is placed in an accessible location for maintenance and monitoring. Regular inspection and testing can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs down the line. Also, familiarize yourself with the valve's manual to understand its functionality and ensure it operates within safe parameters, enhancing the reliability of your system.
Top 10 Pressure Reducing Valves: Essential Features and Benefits
Key Features of Effective Pressure Reducing Valves
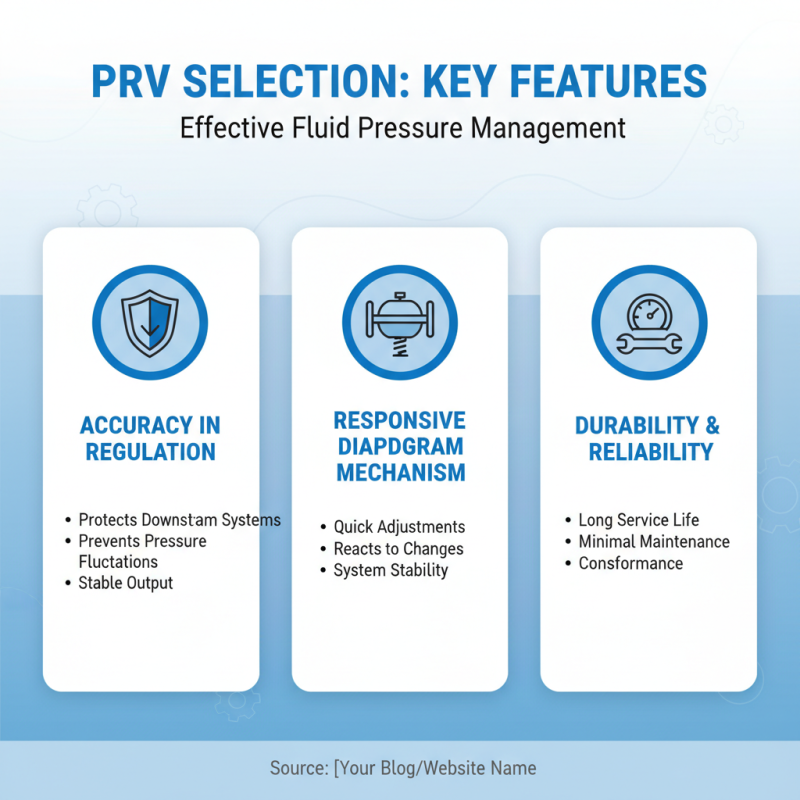
When selecting a pressure reducing valve (PRV), it is essential to understand the key features that contribute to its effectiveness in managing fluid pressure. A well-designed PRV should provide accuracy in pressure regulation, ensuring that downstream systems are protected from pressure fluctuations. Look for valves with a responsive diaphragm mechanism, as they can adjust more quickly to changes, maintaining stability within the system.
Another vital aspect is the material and construction of the valve. High-quality materials are necessary to withstand different environmental conditions and prevent corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability. Additionally, features like a built-in gauge or visual indicators can aid in monitoring performance without the need for additional equipment, streamlining maintenance processes.
Tips for choosing the right PRV include evaluating the specific application requirements, such as the type of fluid and operational pressure range. It's also beneficial to consult with a professional to determine the best size and specifications for your system, as an improperly sized valve can lead to inefficiencies and system failures. Regular maintenance checks are also essential to ensure that the valve continues to operate effectively over time.
Benefits of Using Pressure Reducing Valves in Various Applications
Pressure reducing valves are essential components in various applications, providing significant benefits across multiple industries. One of the primary advantages of using these valves is the regulation of downstream pressure, which protects sensitive equipment and piping systems from potential damage due to excessive pressure. In commercial and industrial settings, maintaining optimal pressure levels ensures smoother operations, prolongs the lifespan of machinery, and reduces the risk of leaks or failures. This is particularly crucial in sectors such as water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Additionally, pressure reducing valves contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings. By controlling the pressure in a system, these valves minimize the energy consumption required for pumping fluids. For instance, in heating and cooling systems, reducing pressure can lead to lower energy costs while improving system performance and comfort. Moreover, in irrigation systems, pressure regulation helps distribute water more evenly, reducing wastage and promoting sustainable water usage. Overall, the implementation of pressure reducing valves not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports environmentally-friendly practices across various applications.
Top 10 Pressure Reducing Valves: Essential Features and Benefits Explained
| Feature | Description | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Adjustment | Allows for precise control of downstream pressure. | Water supply systems, boiler systems. | Improves system efficiency and safety. |
| Flow Control | Regulates flow rate in various systems. | Hydraulic systems, irrigation systems. | Enhances operational performance. |
| Durability | Constructed with robust materials for longevity. | Industrial applications, chemical processing. | Reduces maintenance and replacement costs. |
| Compact Design | Space-saving configurations available. | Manufacturing, HVAC systems. | Ideal for limited space installations. |
| Temperature Resistance | Designed to withstand various temperature ranges. | Heat exchangers, steam systems. | Ensures reliable operation in extreme conditions. |
| Maintenance-Free Operation | Minimal upkeep required for long-term performance. | Residential plumbing, irrigation. | Saves time and resources. |
| Versatility | Can be used across various systems and fluids. | Oil, gas, water treatment. | High adaptability to different applications. |
| Safety Features | Equipped with safety mechanisms to prevent overpressure. | Gas distribution systems, industrial processes. | Enhances system safety and reduces risks. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Reduces energy consumption and operational costs. | Commercial and industrial applications. | Provides long-term savings on operational expenses. |
| Customizable Settings | Adjustable settings for specific operational needs. | Pharmaceuticals, food processing. | Tailors performance to varied applications. |
Selection Criteria for Choosing the Right Pressure Reducing Valve
When selecting the right pressure reducing valve (PRV), it is crucial to consider several key criteria that ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your system. First, assess the pressure range that your application requires. Each PRV is designed to handle specific inlet and outlet pressures, so understanding your system's needs will help you choose a valve that maintains safe and efficient operation.
Additionally, consider the flow capacity; the selected valve should be capable of accommodating your system's maximum flow rate, preventing any bottlenecks or excessive pressure build-up.
Another important factor is the material composition of the valve. Depending on the medium being controlled—such as water, gas, or chemicals—different materials may be more suitable to enhance durability and resistance to corrosion or wear.
Furthermore, the type of actuator can influence performance; options include diaphragms or piston-driven systems, each providing varying levels of sensitivity and response time. Lastly, consider the ease of maintenance and installation. A valve that is user-friendly can save time and costs in the long run, ensuring that the PRV can be easily serviced or replaced when necessary. By carefully evaluating these selection criteria, you can choose a pressure reducing valve that best meets your operational requirements.
Common Maintenance Practices for Pressure Reducing Valves

Maintaining pressure reducing valves (PRVs) is crucial for ensuring their efficiency, safety, and longevity. Proper maintenance practices can significantly reduce the risk of operational failures and costly downtime. According to industry reports, regular inspection and maintenance can extend the lifespan of PRVs by up to 30%, translating to substantial cost savings. Key practices include routine visual inspections, checking for leaks, and ensuring that the valve’s components, such as diaphragms and springs, are in good condition. Additionally, cleaning the valve body and seat to remove any debris or buildup is essential for optimal performance.
Lubrication is often overlooked but is vital in reducing friction between moving parts, thereby preventing wear and tear. Industry studies indicate that properly lubricated valves can operate 20% more efficiently than those that are not maintained in this way. Furthermore, operators should schedule periodic testing to ensure that the pressure settings remain accurate and that the system responds appropriately to changing demands. Implementing these common maintenance practices not only enhances the functionality of pressure reducing valves but also bolsters the overall safety of the system, thereby safeguarding personnel and infrastructure from potential hazards.
Related Posts
-
Exploring Back Pressure Valve Innovations in the Context of China's 138th Canton Fair 2025 Industry Trends
-

10 Best Pressure Valves for Optimal Performance and Durability in 2023
-

10 Reasons Pressure Regulator Valve is Essential for Industrial Applications
-
The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Gas Regulator Valve for Your Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Natural Gas Regulators for Your Home Needs
-

Understanding Industry Standards for Best Slide Gate Valve Manufacturing Processes
