- Products
- Pressure Reducing Regulators
- Back Pressure Regulators
- Tank Blanketing Valves
- Temperature Regulators
- Industrial Control Valves
- Wafer Style Control Valves
- JCVS Industrial Control Valves
- Globe Style/Cage Guided Control Valves
- Mixing/Diverting Control Valves
- Motor Operated Control Valves
- Valve Positioners & Accessories
- Applications
- Resources
- Find a Sales Rep
- Brands
Understanding the Role of Flow Regulator Valves in Modern Fluid Control Systems
In today’s complex fluid control systems, the significance of Flow Regulator Valves cannot be overstated. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global flow control market is projected to reach USD 27.7 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2020. Flow Regulator Valves are pivotal in maintaining precise flow rates, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing energy consumption across various industries, including water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC. The ability to automatically adjust flow rates ensures that systems operate within optimal parameters, minimizing waste and preventing system failures. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and operational efficiency, understanding the role of Flow Regulator Valves in modern fluid control systems becomes essential for engineers and designers aiming to innovate and improve system performance.
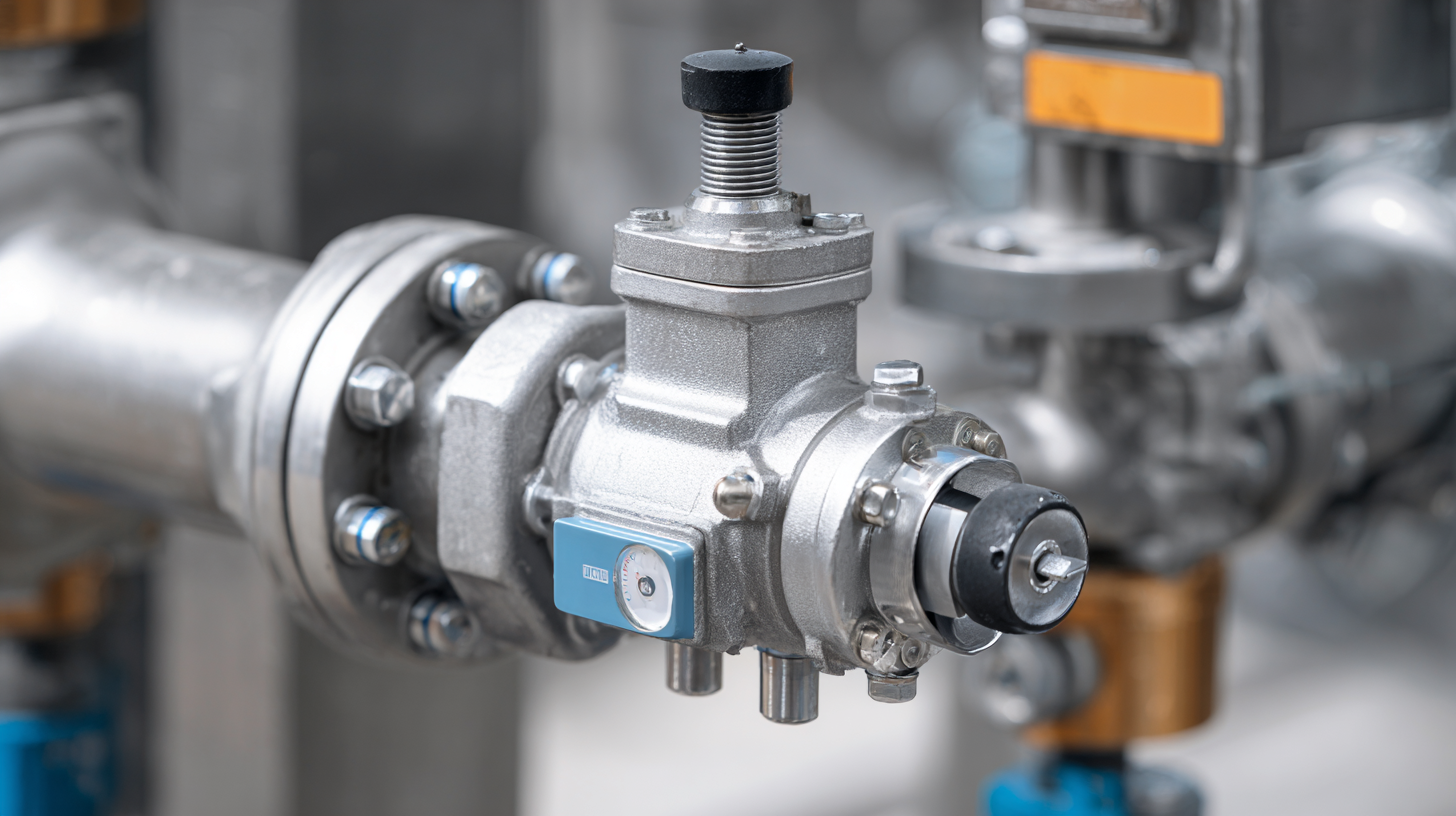
Significance of Flow Regulator Valves in Fluid Control Systems
Flow regulator valves play a pivotal role in modern fluid control systems, influencing efficiency and performance across various industries. According to a report by the Global Flow Control Market Research Institute, the demand for flow control devices, including regulator valves, is projected to reach $33 billion by 2026, a significant growth driven by advancements in industrial automation and the increasing need for optimized fluid management. These valves ensure consistent flow rates regardless of changes in upstream pressure, thereby enhancing system reliability and reducing operational costs.
Furthermore, the integration of flow regulator valves contributes to energy conservation efforts. Studies indicate that systems utilizing these valves can achieve up to a 30% reduction in energy consumption in applications such as HVAC and water management. By maintaining precise flow levels, operators can minimize waste and improve the sustainability of their processes. As industries shift towards more stringent regulatory standards regarding resource usage and emissions, the implementation of flow regulator valves becomes increasingly essential for compliance and efficiency, solidifying their significance in contemporary fluid control systems.
Understanding the Role of Flow Regulator Valves in Modern Fluid Control Systems
| Parameter | Description | Importance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate Control | Regulates the rate of fluid flow in systems. | Essential for maintaining system efficiency and safety. | Hydraulic systems, irrigation systems. |
| Pressure Stabilization | Maintains consistent pressure within the system. | Prevents damage from pressure fluctuations. | Chemical processing, water treatment. |
| Flow Direction Control | Controls the direction of fluid flow within the system. | Crucial for multi-directional systems. | HVAC systems, fuel distribution. |
| Temperature Regulation | Ensures optimal fluid temperature in processes. | Essential for chemical stability and efficiency. | Food processing, HVAC. |
| Safety Mechanisms | Provides emergency shut-off to prevent accidents. | Critical for safety in high-pressure environments. | Oil and gas pipelines, industrial machinery. |
Key Components and Mechanisms of Flow Regulator Valves
Flow regulator valves are essential components in modern fluid control systems, designed to maintain a consistent flow rate despite fluctuations in pressure or varying demand. These valves function by automatically adjusting the flow of fluid through the system, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Key mechanisms within flow regulator valves include throttling and feedback systems, which respond dynamically to changes in system conditions.
One common type of flow regulator valve utilizes a spring-loaded diaphragm that reacts to pressure differentials. When the downstream pressure rises, the diaphragm compresses, reducing the flow area and stabilizing the output flow rate. Conversely, in systems where pressure drops, the diaphragm expands, allowing more fluid to pass through. Additionally, some advanced models incorporate electronic control systems that provide precise adjustments in real time, enhancing the system's responsiveness and accuracy. By understanding these components and mechanisms, engineers can select the appropriate flow regulator valves to meet the needs of specific applications, improving overall fluid management.
Understanding the Role of Flow Regulator Valves in Fluid Control Systems
This chart illustrates the key performance indicators of flow regulator valves in modern fluid control systems, highlighting flow rate, pressure drop, temperature, and energy loss values critical to their operation.
Advantages of Using Flow Regulator Valves in Modern Applications
Flow regulator valves play a crucial role in modern fluid control systems, providing enhanced performance across various applications. These valves maintain consistent flow rates regardless of pressure fluctuations, significantly improving system efficiency. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for flow control valves is expected to reach $18.5 billion by 2026, showing an increasing demand for precision in industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing.
One of the primary advantages of using flow regulator valves is their ability to reduce energy consumption. By ensuring optimal flow rates, these valves minimize the workload on pumps and other equipment, contributing to lower operational costs. A study published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) indicates that integrating flow control solutions can lead to energy savings of up to 30%. Furthermore, their ability to provide stable flow contributes to improved process reliability and product quality, reducing the risk of errors in sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Flow Regulation
Flow regulation is crucial in fluid control systems, yet it often comes with its own set of challenges. One common issue is the fluctuation in flow rates, which can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to systems. These fluctuations can result from varying demand cycles or pressure changes in the supply line. To address this challenge, engineers often integrate advanced flow regulator valves that are equipped with responsive control mechanisms, allowing them to adjust the flow dynamically. Such valves help maintain a consistent flow rate, ensuring operational efficiency.
Another challenge faced by fluid control systems is the buildup of deposits within the valves, which can obstruct flow and reduce system performance. This is particularly prevalent in systems that handle viscous or particulate-laden fluids. To combat this issue, regular maintenance schedules should be established, and the use of self-cleaning valves can be considered. These solutions not only reduce downtime but also improve the reliability of the fluid control system in the long run. Moreover, adopting materials that resist corrosion and scaling can further enhance the longevity and efficiency of flow regulator valves in various operating conditions.
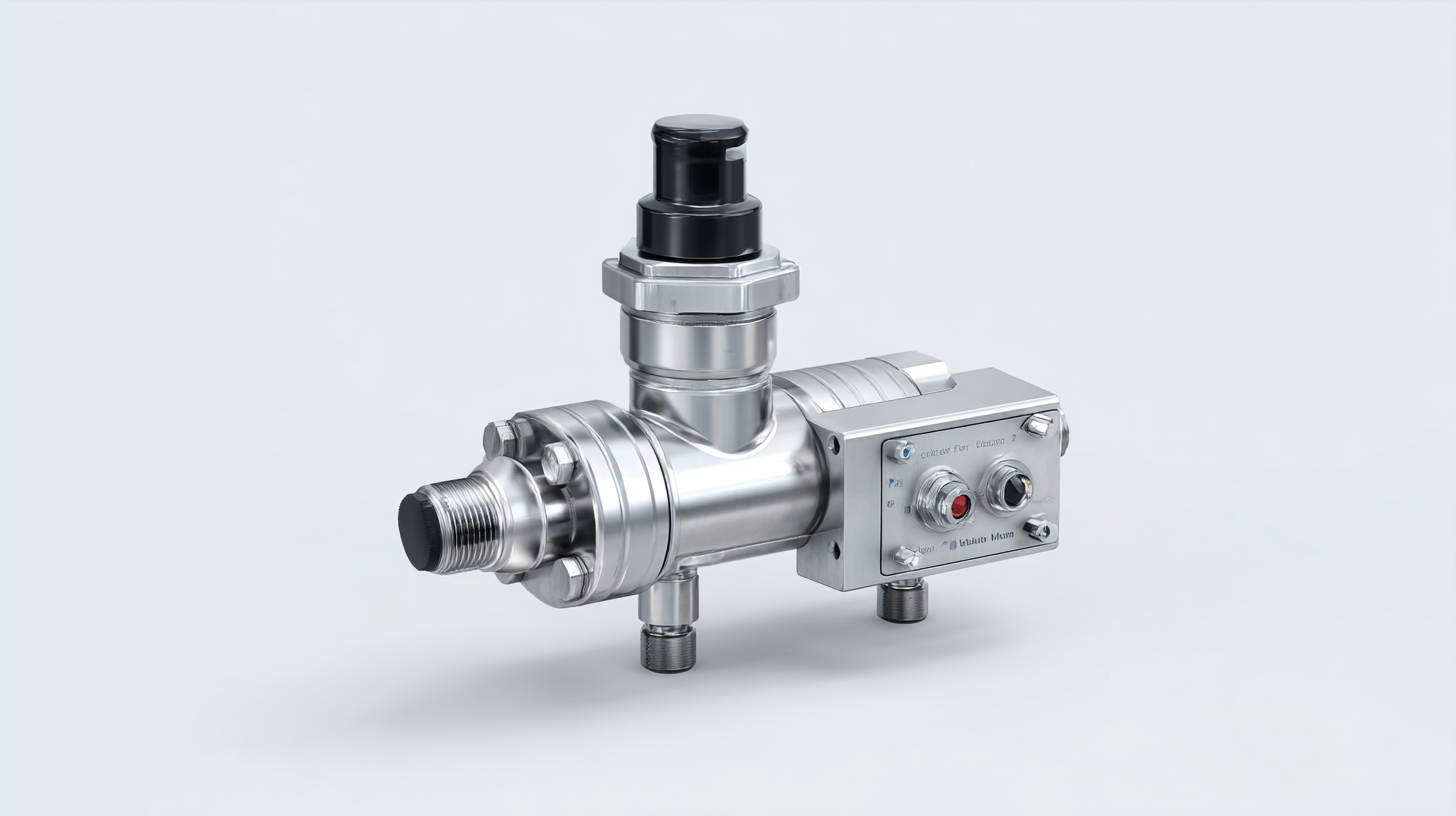

Tips for Selecting the Right Flow Regulator Valve for Your System
When it comes to selecting the right flow regulator valve for your fluid control system, understanding the specific needs of your application is crucial. According to a report by the Flow Control Association, a well-chosen flow regulator valve can enhance system efficiency by as much as 30%. This improvement stems from correctly matching the valve's flow characteristics with the fluid dynamics of the system, ensuring optimal performance and minimal losses.
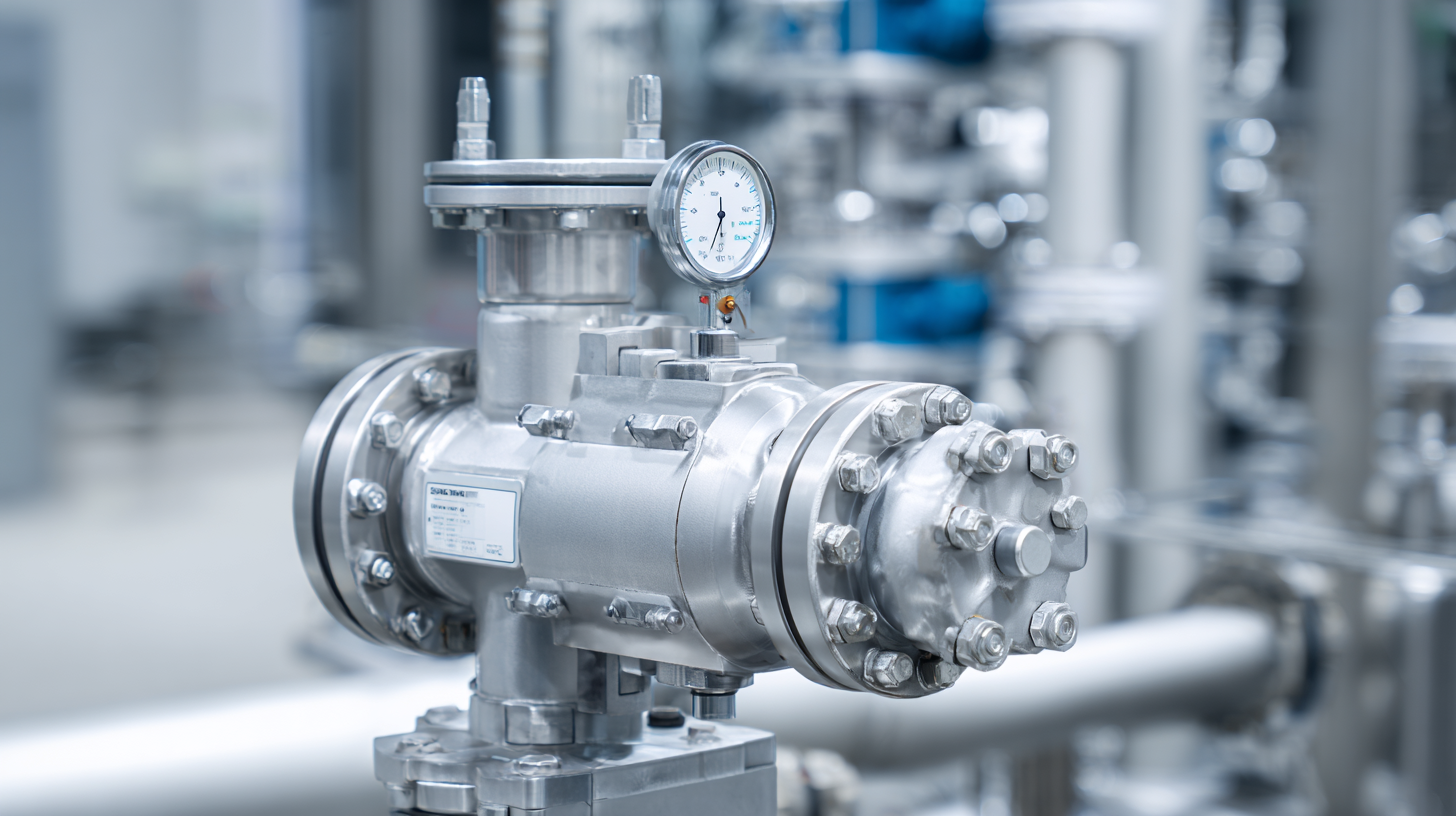

One key consideration in your selection process is the valve's material compatibility with the fluids it will handle. For example, if your system deals with corrosive substances, materials such as stainless steel or PVC could be ideal. Additionally, sizing the valve appropriately is paramount; an oversized valve could lead to fluctuating flow rates while an undersized valve restricts flow, both of which adversely affect system performance. Data from the International Society of Automation indicates that improper valve sizing can account for up to 20% of operational inefficiencies in fluid control systems, making this a critical factor in your selection process.
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize Your System with Flow Regulator Valves for Maximum Efficiency
-

Future Trends in Best Flow Valve Market Analysis for 2025 Industry Outlook
-

Mastering High Pressure Regulation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Best Regulator
-
Top 5 Innovative Applications of the Best High Pressure Regulators in Various Industries
-

How to Choose the Right Water Regulator Valve for Your Industrial Needs
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Pressure Regulator Valves in Industrial Applications
