- Products
- Pressure Reducing Regulators
- Back Pressure Regulators
- Tank Blanketing Valves
- Temperature Regulators
- Industrial Control Valves
- Wafer Style Control Valves
- JCVS Industrial Control Valves
- Globe Style/Cage Guided Control Valves
- Mixing/Diverting Control Valves
- Motor Operated Control Valves
- Valve Positioners & Accessories
- Applications
- Resources
- Find a Sales Rep
- Brands
How to Choose the Right Pressure Regulator for Your Industrial Needs
Choosing the right pressure regulator is crucial for optimizing industrial processes and ensuring safety and efficiency in operations. A pressure regulator is a vital component in systems where maintaining a specific pressure is essential, as it controls the flow of gases or liquids to ensure they remain at desired levels.
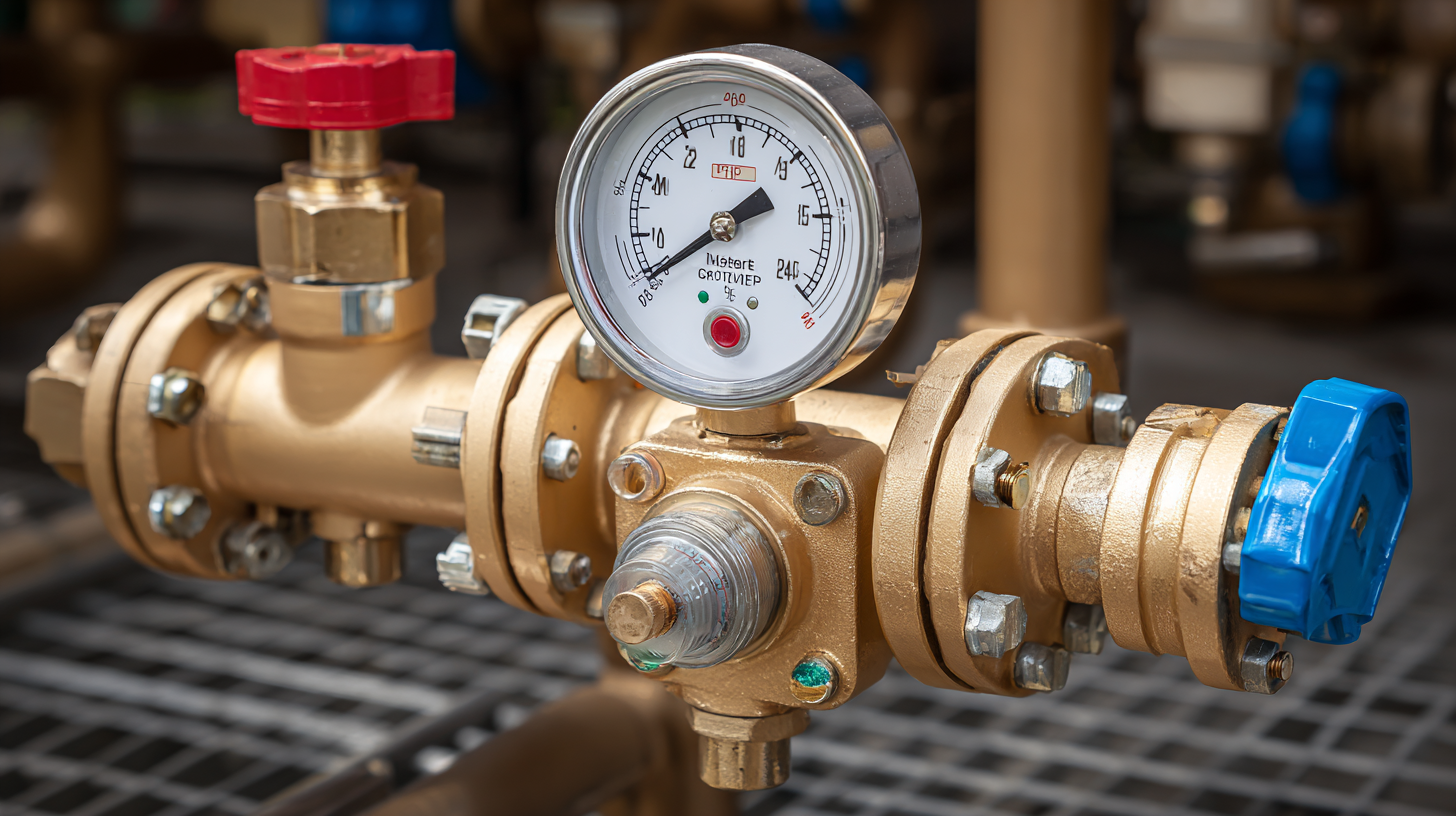 With various types of pressure regulators available, including adjustable, non-adjustable, and back-pressure regulators, understanding the specific requirements of your application is key to making an informed decision. Factors such as the medium being regulated, pressure range, flow rate, and environmental conditions all play significant roles in selecting the most appropriate device.
This guide will provide insights into the essential considerations and best practices to help you identify the right pressure regulator for your industrial needs, ensuring streamlined operations and enhanced safety.
With various types of pressure regulators available, including adjustable, non-adjustable, and back-pressure regulators, understanding the specific requirements of your application is key to making an informed decision. Factors such as the medium being regulated, pressure range, flow rate, and environmental conditions all play significant roles in selecting the most appropriate device.
This guide will provide insights into the essential considerations and best practices to help you identify the right pressure regulator for your industrial needs, ensuring streamlined operations and enhanced safety.
Understanding the Different Types of Pressure Regulators in Industrial Applications
When selecting a pressure regulator for industrial applications, it's essential to understand the different types available and their specific functionalities. There are primarily two categories of pressure regulators: single-stage and two-stage regulators. Single-stage regulators are typically used in applications where a stable outlet pressure is essential but the inlet pressure can fluctuate significantly. They offer quick response times and are often found in smaller systems or where simplicity is key.
In contrast, two-stage regulators provide more precise control over outlet pressure, making them suitable for applications with high inlet pressure variations. The first stage of regulation reduces the pressure to a stable intermediate level, while the second stage fine-tunes the output to the desired pressure. This kind of regulator is ideal for larger systems or critical processes that require consistent pressure for optimal operation. By understanding these types, industries can choose a regulator that best meets their operational needs and enhances system efficiency.
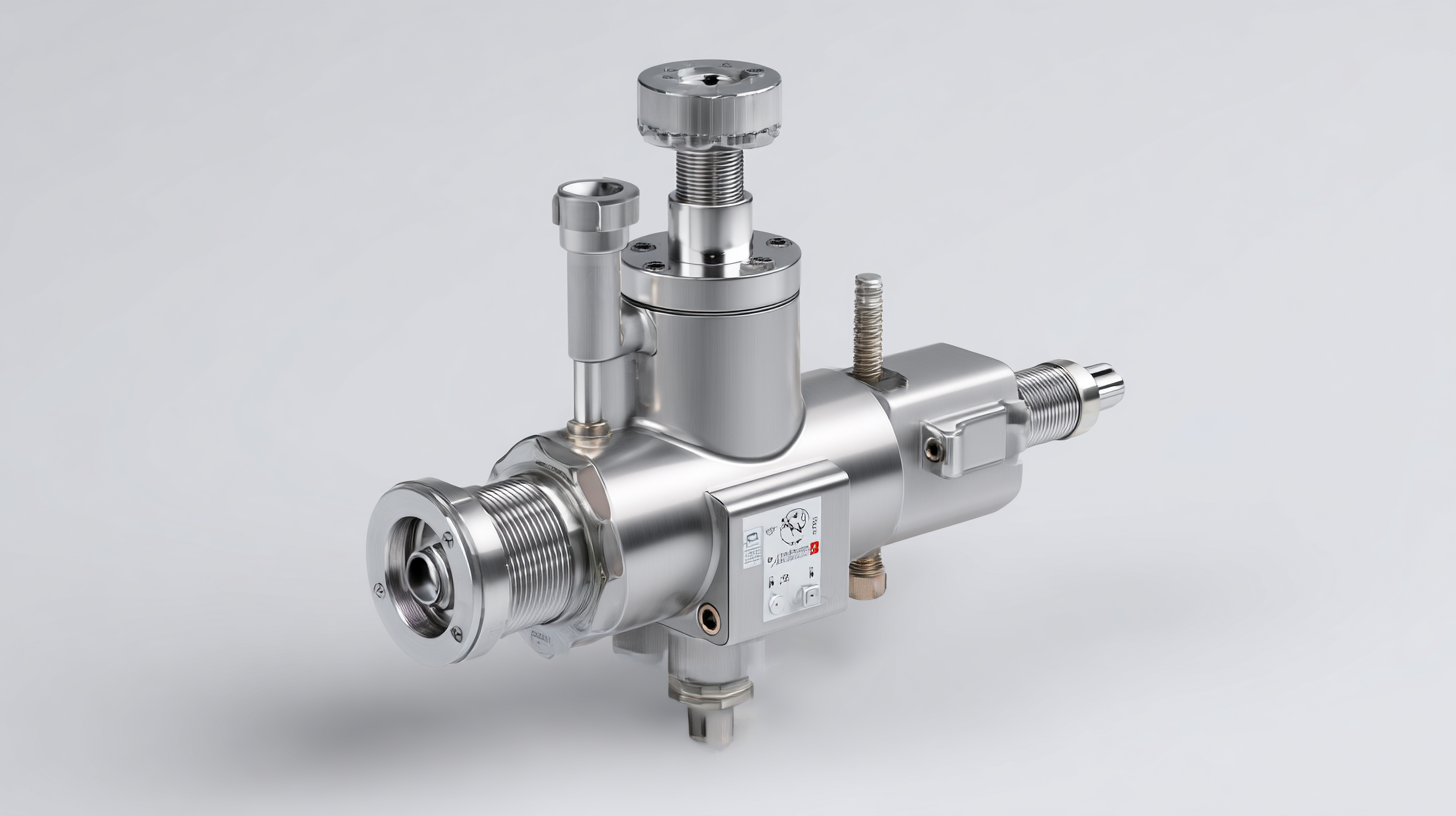

Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a Pressure Regulator
When selecting a pressure regulator for industrial applications, there are several key specifications to consider that will influence performance and reliability. First, understand the operating pressure range required for your processes. The regulator must effectively handle both the maximum and minimum pressures to ensure consistent performance. Additionally, knowing the flow rate needed is crucial, as it directly correlates with the regulator’s capacity to maintain pressure under varying conditions.
Another important specification is the regulator’s construction material. Depending on the application, materials such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic may be more suitable, especially when dealing with corrosive gases or aggressive environments. Furthermore, consider optional features like gauge ports for monitoring and adjusting pressure, and safety features such as relief valves. Assessing these specifications will ensure that the selected pressure regulator not only meets operational requirements but also enhances safety and efficiency in your industrial processes.
How to Choose the Right Pressure Regulator for Your Industrial Needs - Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a Pressure Regulator
| Specification | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Inlet Pressure | The highest pressure the regulator can handle on the inlet side. | 150 - 3500 psi |
| Outlet Pressure Range | The adjustable pressure range available at the outlet. | 0 - 300 psi |
| Flow Capacity | The volume of gas/liquid the regulator can handle over time. | 1 - 500 SCFH |
| Temperature Range | The operational temperature limits for the regulator. | -40°F to 200°F |
| Material | Construction materials suitable for the application environment. | Brass, Stainless Steel, Aluminum |
| Regulator Type | Type of regulator depending on application and gas type. | Single Stage, Double Stage |
The Importance of Flow Rate and Set Pressure in Regulator Performance
When selecting a pressure regulator for industrial applications, understanding both flow rate and set pressure is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Flow rate, measured in units such as liters per minute or cubic feet per hour, directly affects how efficiently a system operates. An insufficient flow rate can lead to inadequate supply for downstream processes, resulting in bottlenecks or system failures. Therefore, it’s essential to determine the maximum and minimum flow rates needed for your specific application.
Equally important is the set pressure, which dictates the pressure level at which the regulator maintains. This parameter must align with the requirements of the equipment connected to the regulator. Choosing a regulator with the wrong set pressure can cause damage to sensitive instruments or result in inefficient operation. A regulator that is not finely tuned to your application’s needs can lead to erratic performance, potentially compromising safety and productivity. Thus, carefully assessing both flow rate and set pressure ensures that you select a regulator that matches your industrial demands, fostering reliable and efficient operations.

Common Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements for Pressure Regulators
When selecting a pressure regulator for industrial applications, understanding common industry standards and compliance requirements is crucial. Different sectors, such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, have specific guidelines to ensure safety and efficiency. Familiarize yourself with regulatory bodies such as ASME, ASTM, and ISO, which outline testing, material, and performance standards for pressure regulators. Compliance with these standards not only guarantees the reliability of your equipment but also prevents potential legal issues.
**Tips:** Always verify that the pressure regulator you choose has the necessary certifications corresponding to your industry's requirements. Regular audits and inspections can further ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
Additionally, consider the specific applications and environments where the regulator will be used. Different industries might require unique features such as corrosion resistance, temperature range, or adjustable pressure settings. This understanding will help in selecting a regulator that meets both operational needs and regulatory compliance.
**Tips:** Assess the manufacturer's reputation and check for customer reviews to ensure that their products consistently comply with industry standards. Providing your team with adequate training on the importance of compliance can also significantly reduce risks associated with improper equipment use.
Pressure Regulator Compliance by Industry Standard
Maintenance Tips for Ensuring Longevity and Reliability of Pressure Regulators
Maintaining pressure regulators is crucial for ensuring their longevity and reliability in industrial applications. According to a report from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), regular maintenance can increase the lifespan of these devices by up to 30%. This involves routine inspections to check for wear and tear, replacing filters, and ensuring that the seals are intact to prevent leaks. High-quality components are essential, as inferior materials can degrade faster, leading to malfunctions and costly downtimes.
In addition to scheduled maintenance, proper calibration of pressure regulators is key to their performance. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) emphasizes that calibrating regulators according to manufacturer specifications every six months can maintain operational efficiency. Furthermore, utilizing data from your facility's monitoring systems can help identify trends that may indicate a need for maintenance before failures occur.
Implementing these best practices not only extends the life of pressure regulators but also enhances system safety and efficiency, contributing to overall productivity in industrial settings.
Related Posts
-

10 Reasons Pressure Regulator Valve is Essential for Industrial Applications
-

Mastering High Pressure Regulation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Best Regulator
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Pressure Regulator Valves in Industrial Applications
-
Top 5 Innovative Applications of the Best High Pressure Regulators in Various Industries
-

Top Strategies for Maximizing Efficiency with High Pressure Regulators
-

How to Choose the Right Natural Gas Regulators for Your Home Needs
